We now have over 20 different types of fillers approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
There is no one-size-fits-all product.
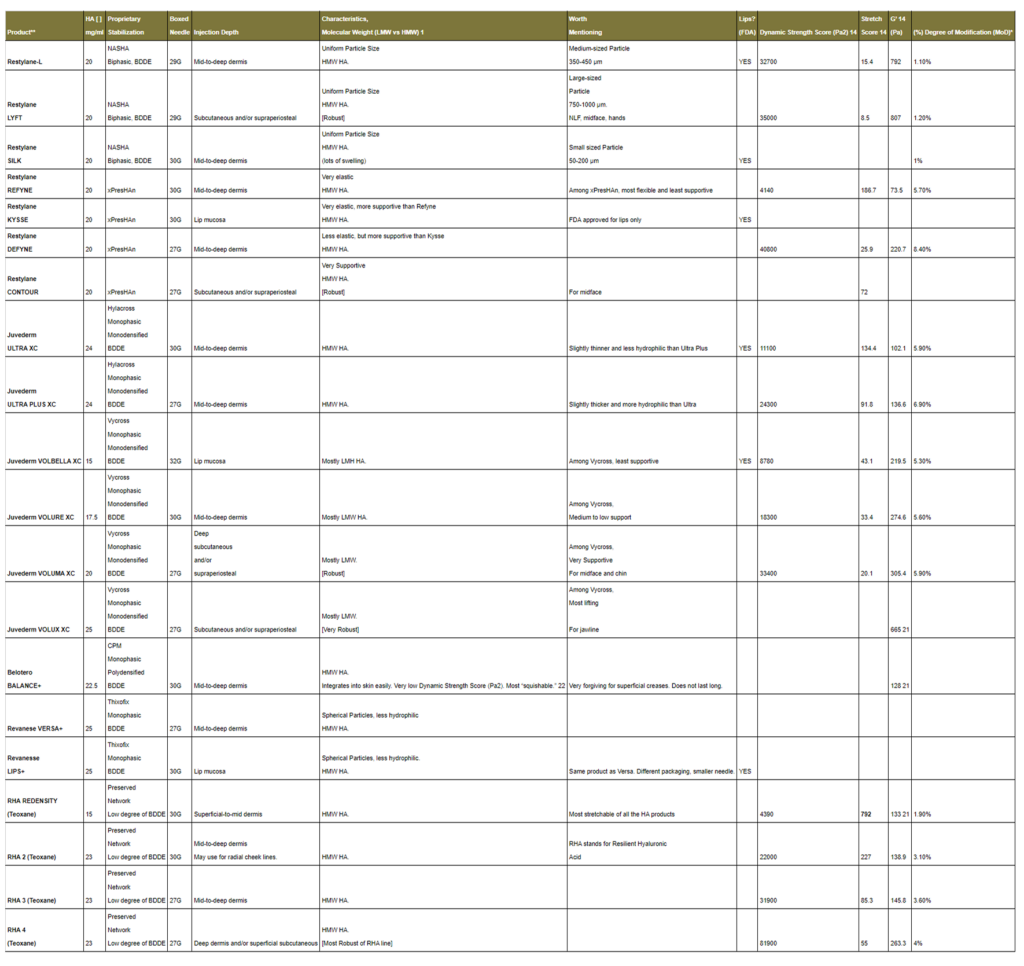
For more details, click on the following table…
LEGEND
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA) A water soluble sugar polymer that belongs to a class of compounds known as glycosaminoglycans. It is made up of long chains of repeating disaccharide units of N-acetylglucosamine and glucuronic acid.18
- HA Chain Length ∝ Molecular Weight HA chain length is associated with (proportional to) the molecular weight of the HA chain.18 Short HA Chains = Low Molecular Weight (LMW), Long HA Chains = High Molecular Weight (HMW).
- Monophasic Cross-links formed between hyaluronic acid chains make a uniform gel-like structure.
- Biphasic Biphasic material consists of 2 or more substances in a blend. In the case of hyaluronic acid, it can exist in two different physical states: cross-linked HA and non-cross-linked HA. Biphasic material is not homogenous (not uniform in character or content).
- (%) Degree of Modification (MoD) Degree of Modification (MoD) is the ratio of chemical crosslinkers that form cross-links to the total number of HA disaccharide units.
- Dynamic Strength Score (Pa2) The Dynamic Strength Score characterizes the ability of a gel to maintain its physical integrity and gel characteristics over a wide range of stress or deformation values15
- Stretch Score (%/s) Stretch is the ability of the gel to deform (e.g., extend) and adapt to dynamic facial movement. The Stretch Score describes the ability of an HA gel to deform without disruption when subjected to continuous pressure.
- G’ (Pa) Elastic modulus or storage module (G’) describes the ability of a gel to rebound to its original shape when a force is applied. High G’ usually correlates with a firmer gel. 16
- 1 Micheels P et al. J Drug Dematol. 2016;15(5):600-606.
- 14 Data on File. RDRE 2016. Newark, CA: Revance Therapeutics, Inc, 2020.
- 15 Faivre J et al. Poster presented at: 2020 IMCAS; January, 2020; Paris, France.
- 16 Fagien S et al. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143:707e-720e.
- 18 Monslow J et al. Front Immunol. 2015;6:231.
- 21 Rheologic and Physicochemical Characteristics of HA Fillers: Overview and Relationship to Product Performance, Facial Plast Surg 2022;38:116–123. It is notable that published G’ values differ depending on the study and information source.
- 22 “Squishable” as an anecdotal observation by Dr. Lum and other injectors when product is injected superficially.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 2018 plastic surgery statistics report, published 2019.